Iron Metabolism in Eukaryotesã¢â‚¬â€mars and Venus at It Again
Balbharti Maharashtra Land Lath Form vi Scientific discipline Solutions Chapter five Substances in the Surround – Their States and Properties Notes, Textbook Exercise Of import Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Lath Class vi Science Solutions Chapter v Substances in the Surroundings – Their States and Backdrop
Class 6 Science Chapter five Substances in the Surroundings – Their States and Properties Textbook Questions and Answers
one. In the paragraph below write 'solid', 'liquid' or 'gas' in each of the blank (brackets) depending on the substance referred to just before.
Question a.
On a bright sunny twenty-four hours, Riya and Gargi are playing with a ball (…..) in the park. Gargi feels thirsty. So, Riya brings tender coconut water (…..) for her. At the aforementioned time, a strong breeze (…..) starts bravado and information technology as well begins to rain (…..). They run back into the firm (…..), change their clothes (…..) and then their female parent gives them a cup (…..) of hot milk (…..) to drink.
Answer:
solid, liquid, gas, liquid, solid, solid, solid, liquid.
![]()
2. Discuss.
Question a.
Riya pours some water from her bottle into another bottle. Does information technology alter the shape of the water?
Answer:
Aye, the shape of water changes as water is in liquid land. Liquids do not take a shape of its own. They take the shape of the container.
Question b.
Halima picks up a small rock from the footing and puts it in the water in a dish. Does the shape of the stone change?
Answer:
No, the shape of the stone does not change. Rock is a solid, hence retains its shape.
3. Write the properties of these substances.
(water, drinking glass, chalk, atomic number 26 ball, sugar, common salt, flour, coal, soil, pen, ink, lather)
Question a.
Write the properties of these substances.
(water, glass, chalk, iron ball, sugar, common salt, flour, coal, soil, pen, ink, soap)
Answer:
Properties of substances:
| Substance | Country | Properties |
| 1. Water | Liquid | Fluidity, density, solubility, transparency, thermal conductivity. |
| two. Glass | Solid | Brittleness, hardness, density, transparency. |
| three. Chalk | Solid | Brittleness, density. |
| 4. Iron ball | Solid | Hardness, density, malleability, ductility, electrical ductility, conductivity, thermal conductivity, luster, sonority. |
| v. Sugar | Solid | Brittleness, density, solubility. |
| half dozen. Salt | Solid | Brittleness, density, solubility. |
| 7. Flour | Solid | Density, solubility. |
| 8. Coal | Solid | Brittleness, density, thermal electrical conductivity. |
| nine. Soil | Solid | Brittleness, density. |
| ten. Pen | Solid | Hardness, density. |
| 11. Ink | Liquid | Fluidity, density, solubility. |
| 12. Soap | Solid | Brittleness, hardness, density, solubility. |
![]()
iv. What is sublimation? Write the names of everyday substances that sublimate.
Question a.
What is sublimation? Write the names of everyday substances that sublimate.
Answer:
- The change of a solid substance directly into a gas or vapour without starting time changing into liquid is chosen sublimation.
- Substances that sublimate: Camphor, napthalene balls, ammonium chloride, iodine.
5. What is fabricated from? Why?
a. A sickle to cutting sugarcane.
b. The sheets used for roofing.
c. A screwdriver
d. A pair of tongs.
e. Electric cables.
f. Ornaments.
g. Pots and pans.
Question a.
A sickle to cut sugarcane.
Respond:
A sickle is made of iron. An iron sickle is hard and malleable. When sharpened it volition be able to cut the hard sugarcane.
![]()
Question b.
The sheets used for roofing:
Answer:
- The sheets used for roofing are made of plastic, aluminium.
- Plastic is hard, hence, protects against weather conditions.
- Plastic is transparent, hence, sunlight can pass through it.
- Aluminium is hard, light weight and durable, hence, protects against all conditions conditions.
- Malleable hence formed into thin sheets.
Question c.
A screwdriver:
Answer:
- A screwdriver is fabricated upward of iron, steel, aluminium.
- A screwdriver possesses property of hardness hence, it easily pierces a screw in piece of wood, wall, metals etc.
Question d.
A pair of tongs:
Answer:
- A pair of tongs are made up of iron, steel aluminium etc. Tongs are used to lift hot, humid utensils or vessels.
- Tongs are hard, ductile and malleable.
- Hence, have potent grip to concord utensils.
- Rubbers fitted on the ends volition protect from thermal conduction, from bums.
![]()
Question e.
Electric cables:
Answer:
- Electric cables are metallic wires (thin) wound in plastic.
- Metal wires possess the property of hardness, ductility, electrical conductivity.
- Plastic /rubber covering possesses the property of hardness, elasticity and are bad conductors of heat and electricity.
Question f.
Ornaments:
Answer:
- They are made up of metals like golden and silver.
- They possess the property of hardness, ductility, malleability, lustre.
Question one thousand.
Pots and pans: Reply:
- They are used to melt food, hence metals like aluminium, steel are used.
- They possess the property of hardness, ductility, malleability, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, (microwave ovens)
6. What will happen if ….? And why?
Question a.
Nails are fabricated of plastic
Answer:
If nails are made of plastic, they will not be able to pierce through other substances on being pushed or forced by a hammer. Plastic lacks the property of hardness.
![]()
Question b.
A bong is fabricated of wood.
Answer:
- If a bell is fabricated of woods it will never brand a ringing sound. A wooden bell does not accept the holding of existence sonorous.
- Sonority is the property of metals to produce a ringing sound.
Question c.
Rubber is not fitted on a pair of tongs.
Reply:
- Condom is a bad conductor of heat and electricity. It volition not allow heat to pass to the hands/handle of the tongs, thus protecting united states of america.
- Pair of tongs are made up of metals which carry heat and electricity. They have file property of thermal conduction and electrical conduction.
- If rubber is not fitted on a pair of tongs, nosotros volition non be able to elevator hot objects with it.
Question d.
A knife is made of wood.
Respond:
Woods does not have the property of malleability. Therefore, the edge of wooden knife will be edgeless. Hence, we will not exist able to cut anything with it.
Question east.
An axe is made of rubber.
Answer:
- If an axe is made of rubber, information technology will not be used to cutting wood or tree.
- Rubber does not accept the property of hardness that is required to push through to cut it.
![]()
7. Who am I?
Question a.
I'chiliad institute in a thermometer, I measure your temperature.
Answer:
Mercury
Question b.
I make things hot or cold.
Respond:
Heat
Question c.
I take no shape whatsoever!
Answer:
Liquid, gases
![]()
Question d.
I deliquesce in water, simply non in kerosene.
Answer:
Salt
viii. Why does this happen?
Question a.
Coconut oil thickens in winter.
Reply:
Coconut oil is in liquid state. In winter the surrounding temperature / atmospheric temperature starts decreasing. Coconut oil starts cooling or losing oestrus, it changes to solid state.
Thus coconut oil thickens in winter.
Question b.
Kerosene left open in a dish disappears.
Respond:
When kerosene is left open in a dish, it is exposed to surrounding temperature. Equally the temperature is more, kerosene starts continuously evaporating and finally disappears.
![]()
Question c.
The fragrance of incense sticks lighted in 1 corner of a room spreads to the other corner.
Respond:
The fragrance of incense sticks is given out in the course of scented vapours. Equally vapours are in gaseous country, the gas molecules spread out in the room. The molecules of gas motion very fast and there are no forces to stop them from going apart. Therefore the fragrance of incense sticks lighted in 1 corner of room spreads to the other corner.
Question d.
What you see in the moving picture.
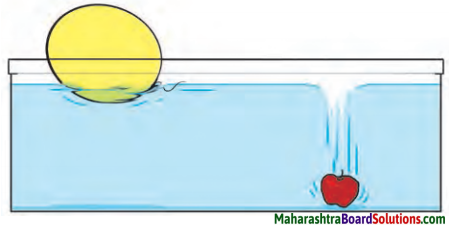
Answer:
The mass of plastic ball is less than an apple. This difference is because of their densities. Since an apple has greater density, it will sink to the bottom on other hand the plastic ball has lesser density, it will float over h2o surface.
![]()
Activity:
Question 1.
Find out how the big statues of wax are made.
Question 2.
Visit a jeweller's store and discover out how ornaments are made.
Class 6 Scientific discipline Affiliate 5 Substances in the Surroundings – Their States and Properties Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
The state of a substance changes if it is …………… or …………… .
Respond:
heated, cooled
Question 2.
Every substance in our surroundings is plant in either the ……………, …………… or gaseous state.
Reply:
solid, liquid
Question 3.
On …………… heat, the substance changes from solid to liquid and liquid to gas.
Reply:
gaining
![]()
Question 4.
When the substance cools, or …………… rut, it changes from gaseous to liquid and liquid to solid state.
Respond:
loses
Question 5.
A …………… corporeality of heat must be gained or lost before the state of a substance tin change.
Answer:
specific
Question half dozen.
When a substance gets rut, it becomes …………… and then …………… .
Reply:
warm, hot
Question vii.
If the substance is very hot, we could get …………… .
Reply:
scalded
Question 8.
A thermometer is used to measure …………… .
Answer:
temperature
Question ix.
…………… is the unit of measuring temperature.
Reply:
Degree Celsius (°C)
![]()
Question 10.
Present, …………… thermometers are frequently used.
Respond:
digital
Question eleven.
Solids have a shape of its …………… .
Answer:
own
Question 12.
Solids have a …………… volume.
Answer:
definite
Question thirteen.
Liquids accept the shape of the …………… .
Reply:
container
Question 14.
Liquids have a …………… book.
Respond:
specific
Question 15.
Air occupies all the available …………… .
Reply:
infinite
![]()
Question 16.
Evaporation occurs from the …………… of the water.
Answer:
surface
Question 17.
At sea-level, pure water boils at …………… .
Reply:
100°C
Question 18.
Condensation of steam takes place at …………… .
Reply:
100°C
Question nineteen.
The temperature of a substance can fall below …………… .
Respond:
0°C
Question 20.
Ice melts at …………… .
Answer:
0°C
![]()
Question 21.
Each substance has a specific boiling point which is too its …………… point.
Answer:
condensation
Question 22.
Each substance has a specific melting betoken which is the same every bit its …………… point.
Reply:
freezing
Question 23.
Candles are made by melting …………… wax.
Reply:
paraffin
Question 24.
Solid carbon-dioxide is …………… .
Answer:
dry ice
Question 25.
Liquid …………… is used in beast husbandry.
Respond:
nitrogen
![]()
Question 26.
Sand is melted to make …………… .
Answer:
glass
Question 27.
Atomic number 26 is melted to make …………… .
Answer:
tools
Question 28.
Substances can exist identified by studying their …………… .
Respond:
properties
Question 29.
Substances that suspension into modest particles are said to be …………… .
Answer:
breakable
![]()
Question 30.
The …………… of any liquid is determined by how easily information technology flows.
Reply:
fluidity
Question 31.
Between substances of the same volume, the ones with greater density are …………… than those of lesser density.
Answer:
heavier
Question 32.
The property of a substance of getting …………… is called its solubility.
Answer:
dissolved
![]()
Question 33.
Minerals from the earth'due south chaff are …………… to obtain metals.
Answer:
processed
Question 34.
Metals can exist converted into …………… by hammering.
Answer:
sheets
Question 35.
Metals tin can exist stretched and drawn into …………… .
Answer:
wires
Question 36.
All metals are …………… of electricity to a greater or lesser extent.
Answer:
conductors
![]()
Question 37.
Every metal has a …………… colour by which it can exist identified.
Answer:
specific
Question 38.
Metals produce …………… sound.
Answer:
ringing
Question 39.
Metals course a …………… group of substances.
Respond:
split
Question 40.
Heat is the cause of the change of the state of …………… .
Reply:
substances
![]()
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column 'A' | Column 'B' |
| one. Humid water | a. > 35° C |
| 2. Torso temperature | b. 0° C |
| three. Freezing water | c. < 5° C |
| four. Air (summer afternoon) | d. < 15° C |
| 5. Inside a fridge | e. < -xviii° C |
| 6. Air (winter night) | f. 100° C |
| 7. Inside the freezer | thou. 37°C |
Answer:
| Column 'A' | Column 'B' |
| i. Boiling h2o | f. 100° C |
| 2. Body temperature | chiliad. 37°C |
| 3. Freezing water | b. 0° C |
| 4. Air (summer afternoon) | a. > 35° C |
| 5. Inside a fridge | c. < v° C |
| 6. Air (winter dark) | d. < fifteen° C |
| 7. Inside the freezer | e. < -xviii° C |
![]()
Reply in 1 sentence:
Question i.
What is modify of state of substances?
Respond:
When a substance changes from i state to another, the procedure is called alter of country of the substance.
Question 2.
When does state of substance change?
Answer:
Land of substance changes when it is heated or cooled.
Question iii.
In which state do substances be in our surroundings?
Answer:
The substances exist in solid, liquid and gaseous form in our environs.
![]()
Question 4.
What happens when a substance gains heat?
Answer:
When a substance gains heat, it changes its state i.east. from solid to liquid and liquid to gas.
Question 5.
What happens when a substance loses heat?
Answer:
When a substance loses heat, it changes its state from gaseous to liquid and liquid to solid state.
Question half dozen.
How do we tell how hot or cold a substance is?
Reply:
The temperature on the thermometer will tell us how hot or cold a substance is.
![]()
Question 7.
What is the unit of measuring temperature.
Answer:
Degrees Celsius (°C) is the unit of measuring temperature.
Question 8.
What is the boiling point of water?
Answer:
The boiling point of water is 100° C.
Question 9.
What is condensation?
Answer:
When vapour cools, it is converted into liquid once more. This process is condensation.
Question x.
At what temperature condensation of steam takes identify?
Answer:
Condensation of steam takes place at 100° C.
Question eleven.
What is the freezing point of water?
Answer:
0° C is the freezing point of water.
![]()
Question 12.
What is the temperature of air in the freezer of a fridge?
Respond:
-18° C is the temperature of air in the freezer of a refrigerator.
Question 13.
At what temperature water ice melts?
Answer:
Ice melts at 0° C.
Question fourteen.
How are candles made?
Reply:
Candles are made by melting alkane wax.
Question 15.
What is the use of solid carbon-dioxide?
Answer:
Solid carbon-dioxide (dry out ice) is used to make ice cream and to keep information technology frozen.
Question 16.
What is the use of liquid nitrogen?
Reply:
Liquid nitrogen is used in animal husbandry.
![]()
Question 17.
What is sublimation?
Reply:
The modify of a solid substance direct into gas or vapour without changing into a liquid is called sublimation.
Question 18.
Ascertain brittleness / What is brittleness?
Answer:
Some substances suspension into modest pieces or particles. Such substances are said to exist brittle. This property of substances is chosen brittleness.
Question 19.
Define hardness / What is hardness?
Respond:
The hardness of a substance is adamant by how much resistance it offers to the substances existence pushed through information technology.
Question 20.
Define elasticity / What is elasticity?
Answer:
Some substances change their shape when a strength is applied on them simply return to their original shape and size when the forcefulness is removed. This belongings is called elasticity.
Question 21.
Define fluidity / What is fluidity?
Answer:
Liquids flow downwardly on a sloping surface. This property is chosen fluidity.
![]()
Question 22.
How is fluidity of any liquid determined?
Answer:
Fluidity of any liquid is determined past how easily it flows.
Question 23.
Ascertain density / What is density?
Answer:
The mass of unlike substances having the same volume can be different. This difference is considering of the difference in their densities. Between substances of the same volume, the ones with greater density are heavier than those of lesser density.
Question 24.
Define solubility / What is solubility?
Respond:
The property of a substance of getting dissolved is chosen its solubility.
Question 25.
Define transparency / What is transparency?
Reply:
When we tin look through a substance and see things on the other side, then that substance is said to be transparent. This property of the substances is chosen transparency.
![]()
Question 26.
Listing some transparent substances.
Respond:
Glass, air, clean h2o and some types of plastic are transparent substances.
Question 27.
What are metals?
Respond:
Metals are substances like copper, gold, atomic number 26, aluminium. They are establish in the course of minerals deep within the world. Minerals from the earth's crust are processed to obtain metals.
Question 28.
Define malleability. / What is malleability?
Answer:
Metals can exist converted into sheets by hammering. This holding of metals is chosen malleability.
Question 29.
Define ductility. / What is ductility?
Respond:
Metals can be stretched and drawn into thin wires. This property of metals is called ductility
![]()
Question thirty.
Name some ductile metals.
Answer:
Metals like silver, gold, platinum can be fatigued into fine wires.
Question 31.
Ascertain electric electrical conductivity. / What is electrical conduction?
Answer:
Electricity flows through metals. All metals are conductors of electricity to a greater or lesser extent.
Question 32.
Define thermal conductivity. / What is thermal electrical conductivity?
Answer:
Metals allow heat to menstruation through them. This property is called thermal conductivity
Question 33.
What is lustre?
Reply:
The typical smooth or characteristic colour by which metal can be identified is chosen lustre.
Question 34.
What is sonority of metals? / Define sonority.
Respond;
Metals produce a ringing sound. This property is chosen the sonority of metals.
![]()
Give scientific reasons for post-obit:
Question 1.
Metals are used to brand musical instruments.
Answer:
Metals possess the property of existence sonorous, i.e. produce a ringing audio. Hence, they are used to make musical instruments.
Question two.
Ornaments are fabricated up of metals.
Respond:
Metals have the property of beingness malleable, ductile, lustrous. Hence, ornaments are made upwards of metals.
Question 3.
Why should we not put our hand or finger in the water to approximate the hotness of water?
Answer:
Nosotros should never put our hand or finger in the h2o to gauge how hot it is because that is not an accurate measure. Besides if the substance is very hot, we could get scalded.
![]()
Can yous tell?
Question 1.
Why are electrical boards fitted on the wall made of plastic or wood?
Respond:
Plastic or wood are bad conductors of estrus and electricity. Electric boards are made up of plastic or woods. Then that while touching nosotros will not get electrical shock.
Question 2.
The handle of cooker is made of plastic. Why?
Answer:
Cooker is fabricated of metallic. When food is cooked in information technology, it gets heated and the whole of its trunk becomes hot due to thermal electrical conductivity. Hence with the plastic handle we tin easily elevator the hot cooker equally plastic is a bad conductor of rut.
Question 3.
Employ your brain ability!
On opening a box of camphor, its smell spreads all around. Why does this happen?
Answer:
- Camphor is a sublimate substance.
- When a box of camphor is opened it changes its state from solid to gas or vapour country.
- This change takes due to the procedure of sublimation where camphor absorbs heat from surrounding to change from solid to gaseous state.
- Camphor particles in gaseous state start spreading all around.
- Hence on opening a box of camphor its smell spreads all around.
![]()
Question four.
Identify the objects shown in fig. five.fourteen. From which substances are they made? What are these substances called as a group?
Answer:
In fig five.14, the metallic bars are shown, these bars are made up of shiny solid. These substances are called metals.
Question five.
Name the solid, liquid and gaseous states of water.
Answer:
- Solid- Ice
- Liquid – water
- Gas – water vapour.
Question six.
Read this list of substances:
spirit, camphor, petrol, ghee, coconut oil, naphthalene balls, ammonium chloride (navsagar).
Question a.
Which 1 freezes in winter?
Respond:
Coconut oil, ghee.
Question b.
Which liquids accept y'all seen change into a vapour?
Answer:
Spirit, petrol.
![]()
Question c.
Which solid directly changes into gaseous country?
Respond:
Camphor, naphthalene balls, ammonium chloride.
Question vii.
The chart given below shows the humid point and freezing signal of some substances. Country whether these substances are solid, liquid or gaseous at room temperature.
| Substance | Freezing Point | Boiling Point |
| Candle | threescore °C | 350 °C |
| Plastic | > 250 °C | 954 °C |
| Iron | 1535 °C | 2862 °C |
Respond:
Candle, plastic and fe are in solid state at room temperature.
![]()
Distinguish between solids, liquids and gases.
Respond:
| Solids | Liquid Gases | |
| e.g.: A piece of iron | e.g.: Water, spirit, oil | e.g.: Air |
| Has a shape of its own, Retains shape, no affair how it is kept. | Does not have a shape of its own. Takes the shape of the container. | Does not have a shape of its own. Occupies all the available space. |
| Has a definite volume. Solids like sugar, sand when poured on a flat surface, form a heap. | It has a specific book. Occupies definite portion of a container. Spreads on a flat surface on pouring. Flows downwards along a slope. Takes the shape of the surface. | Does not have a definite volume. On irresolute the pressure on a gas in a closed container, its book as well changes. |
Distinguish betwixt Humid and Melting.
Answer:
| Boiling | Melting |
| 1. When estrus is supplied to liquids, they boil. | one. When estrus is supplied to solids, they cook. |
| 2. Boiling leads liquids to vapour/gaseous state. | 2. Melting leads solids to liquid land. |
| 3. The temparature at which liquid starts humid continuously is called humid point. | iii. The temperature at which solid turns to liquid completely is called melting betoken. |
![]()
Reply the following briefly:
Question 1.
List properties of solids
Reply:
- Solids have its own shape i.e. Retains shape, no matter how it is kept.
- Solids have definite book.
- e.g. Sand when poured on a flat surface course a heap.
Question two.
List backdrop of liquids.
Answer:
- Liquid does not take a shape of its ain. Takes the shape of the container.
- A liquid has a specific volume i.e. occupies definite portion of a container.
- Liquids: east.thou. water, milk, kerosene.
Question 3.
Listing properties of gases.
Answer:
- Gases does non accept a shape of its own.
- Occupies all the available infinite.
- Does not have a definite volume.
- e.g. Air.
Question 4.
Explicate with case how liquids take the shape of the surface.
Respond:
Liquids accept a specific volume. They occupy definite portion of a container. Liquids spreads on a flat surface on pouring. Liquids catamenia downwards forth a slope.
![]()
Question v.
Explain Ebullition.
Answer:
- As the water gets heated, its temperature increases and it evaporates at a faster and faster rate.
- When water kept on a stove attains a particular temperature or level of heat, then evaporation takes place in all parts of the trunk of water.
- Then we see water bubbles rising at a faster and faster charge per unit to the surface and steam mixing in the air.
- This is called boiling of water or Ebullition.
Question 6.
Explain: Boiling indicate and condensation betoken of water are ane and the aforementioned.
Answer:
Water boils at 100°C. i.e. boiling bespeak of water is 100°C. Condensation of steam also takes place at 100° C. Thus boiling point and condensation signal of water are i and the same.
Question 7.
Explain freezing point of water.
Reply:
- Water kept in a fridge or on ice becomes cooler and libation i.eastward. its temperature falls.
- At a certain temperature water does non cool farther just starts freezing and forms water ice.
- The temperature at which this happens is chosen the freezing point of water. (0° C)
![]()
Question viii.
Explain: Freezing indicate and melting point of water are same.
Reply:
- The temperature at which h2o does not go whatsoever cooler but starts freezing and forming water ice is 0° C.
- When ice gets oestrus, information technology starts melting or changes into liquid state at 0° C.
- Thus, freezing point and melting bespeak of h2o are one and the same.
Question nine.
List various uses of changes in physical state.
Respond:
- Candles are made past melting paraffin wax.
- Solid carbon-dioxide (dry ice) is used to make ice-cream and to keep information technology frozen.
- Liquid nitrogen is used in creature husbandry.
- Sand (silica) is melted to make glass.
- Metals like gold and silver are melted to make ornaments.
- Atomic number 26 is melted to brand tools.
Question 10.
List the properties of substances:
Answer:
The properties of substances are
- Brittleness
- Hardness
- Elasticity
- Fluidity
- Density
- Solubility
- Transparency
![]()
Question 11.
Listing properties of metals:
Respond:
The properties of metals are
- Malleability
- Ductility
- Electrical electrical conductivity
- Thermal conductivity
- Lustre
- Sonority
Question 12.
How can we alter the volume of a gas?
Respond:
On changing the force per unit area on a gas in a closed container we tin can change its volume.
Tin yous tell?
Question 1.
Does water change into vapour the moment nosotros place the vessel on a stove? Does water kept in fridge change at in one case into ice?
Respond:
No, information technology doesn't. H2o slowly changes from one state to another.
![]()
Question 2.
How practise we tell how hot or common cold a substance is?
Respond:
A thermometer is used to measure out the temperature of the subatance which tell usa hot or common cold it is.
Question iii.
How will you lot identify the following
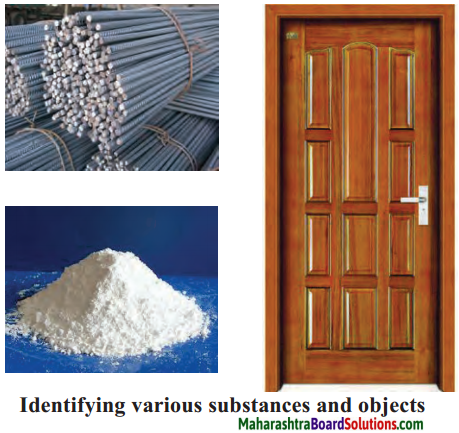

Question i.
A glass: Is it made of plastic, steel or glass?
Answer:
Glass is made of glass as it is transparent.
Question 2.
A rod: Iron or aluminium.
Answer:
A rod is made of iron every bit it is heavy.
![]()
Question iii.
A door: Wooden or drinking glass?
Answer:
A door is wooden as it is opaque.
Question iv.
A white powder: Salt or chalk pulverization?
Answer:
If pulverization dissloves in water it is salt and if it does not dissolves in h2o information technology is chalk.
Source: https://maharashtraboardsolutions.in/category/class-6/page/10/
0 Response to "Iron Metabolism in Eukaryotesã¢â‚¬â€mars and Venus at It Again"
Post a Comment